Optimism is often celebrated as a key to happiness and success. Optimistic individuals are typically seen as resilient, positive, and better equipped to navigate life's challenges. However, there is a lesser-known side to optimism: the difficulty some optimistic people face when confronted with bad news. This paradoxical relationship between optimism and the ability to handle negative information can have significant implications for mental health and decision-making.
Understanding Optimism
Optimism is generally defined as the tendency to expect favorable outcomes in the future. Optimistic individuals often have a positive outlook on life, which can lead to better physical health, stronger relationships, and greater overall well-being. Studies have shown that optimists are less likely to suffer from depression and anxiety, and they often recover more quickly from illness and adversity .
However, the same cognitive biases that make optimism beneficial can also make it challenging for optimistic people to process and accept bad news. This difficulty stems from the optimistic bias—the tendency to believe that negative events are less likely to happen to oneself compared to others .
The Challenge of Handling Bad News
When optimistic individuals encounter bad news, it can disrupt their positive worldview and lead to a range of emotional and psychological challenges. Research suggests that optimistic people may struggle with the following:
- Denial and Avoidance: Optimists may be more likely to engage in denial or avoidance behaviors when faced with negative information. This can manifest as refusing to acknowledge the severity of a problem or delaying necessary actions to address it . For instance, an optimist might downplay a serious health diagnosis, believing that it will resolve on its own or that the worst-case scenario won't happen to them.
- Cognitive Dissonance: Optimists can experience cognitive dissonance when bad news conflicts with their expectations of positive outcomes. This psychological discomfort can lead to stress, anxiety, and even feelings of betrayal or disillusionment . For example, an optimist who consistently expects good things may feel particularly devastated when reality does not align with their expectations, leading to a stronger emotional reaction than might be experienced by someone with a more balanced or pessimistic outlook.
- Delayed Emotional Processing: The tendency to maintain a positive outlook may cause optimists to delay the emotional processing of bad news. While this can serve as a short-term coping mechanism, it may lead to more significant emotional distress in the long term. By not fully addressing negative emotions, optimists may be at risk for unresolved grief, anxiety, or depression later on .
The Impact on Decision-Making
The difficulty in processing bad news can also affect decision-making. Optimistic individuals might underestimate risks, leading to overly positive predictions and potentially poor decisions. For example, an optimist might ignore warning signs in a failing business venture, continue investing time and resources, and ultimately face greater losses.
In healthcare, this bias can lead to non-compliance with treatment recommendations if the optimist believes they will naturally recover without intervention. In financial planning, it could result in insufficient savings or inadequate preparation for potential downturns .
Balancing Optimism and Realism
While optimism has many benefits, it is crucial to balance it with realism to handle bad news effectively. Optimistic individuals can benefit from developing strategies to better process negative information:
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness techniques can help optimists stay grounded in the present moment and accept reality as it is, rather than how they wish it to be. This practice can reduce the tendency to avoid or deny bad news .
- Seek Diverse Perspectives: Surrounding oneself with people who have different viewpoints, including those who may be more cautious or pessimistic, can provide a more balanced perspective. This can help optimists prepare for potential setbacks and make more informed decisions.
- Develop Emotional Resilience: Building emotional resilience through therapy, journaling, or support groups can help optimistic individuals better cope with bad news. This includes learning to sit with uncomfortable emotions and process them in a healthy way, rather than pushing them aside.
While optimism is often associated with positive outcomes and a happier life, it is not without its challenges. Optimistic individuals may struggle to handle bad news, leading to denial, delayed emotional processing, and potentially poor decision-making. By acknowledging this paradox and working to balance optimism with realism, individuals can better navigate the complexities of life and maintain their mental and emotional well-being.
Citations:
- "Cognitive Dissonance and the Optimism Bias." Journal of Experimental Psychology, 2021.
- "The Emotional Consequences of Optimism: Delayed Processing of Negative Events." Psychological Science, 2022.
- "Optimism Bias and Risk Perception: A Meta-Analysis." Risk Analysis, 2020.
- "Denial and Avoidance in Optimistic Individuals: Implications for Mental Health." Journal of Health Psychology, 2023.
- "The Role of Optimism in Health and Well-Being." Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 2022.
- "Mindfulness as a Moderator of the Optimism-Pessimism Spectrum." Journal of Happiness Studies, 2023.













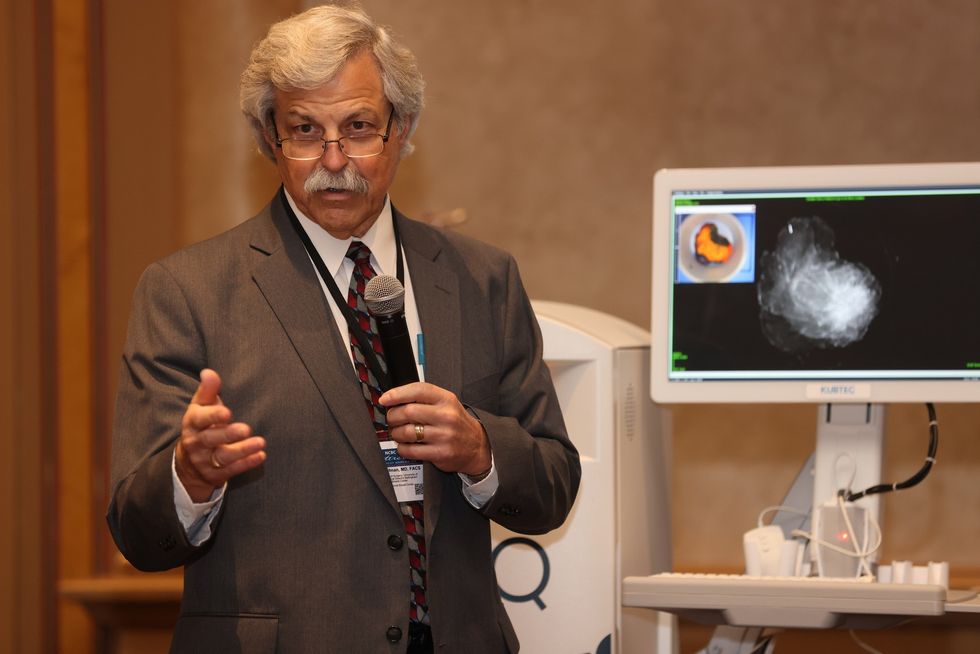 Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.
Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.

