In recent years, concerns about mental health have become increasingly prevalent, particularly among Generation Z, those born between the mid-1990s and early 2010s. This generation, also known as Gen Z, faces a unique set of challenges that can significantly impact their mental well-being. From the pressures of social media to the uncertainties of the modern world, Gen Z is navigating a complex mental health landscape, many of which they struggle through alone.
The Impact of Social Media:
One of the defining characteristics of Gen Z’s upbringing is their immersion in technology and social media from a young age. While social media platforms offer opportunities for connection and self-expression, they also present challenges that can negatively impact mental health. Studies have linked excessive social media use to increased feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression among Gen Z individuals (Twenge & Campbell, 2018). The pressure to curate a perfect online persona can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem, contributing to mental health issues.
Academic Stress and Performance Pressure:
Gen Z faces intense academic pressure, driven by a competitive job market and societal expectations for success. High academic expectations, coupled with the fear of failure, can lead to stress, anxiety, and burnout among students. According to a survey conducted by the American Psychological Association (APA), Gen Z reports higher stress levels than older generations, with academic concerns being a significant source of stress (APA, 2020). The pressure to excel academically can take a toll on mental health, impacting sleep, mood, and overall well-being.
Economic Uncertainty and Future Concerns:
Gen Z is coming of age in a world marked by economic instability and uncertainty. The aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, coupled with the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, has shaped their outlook on the future. Many Gen Z individuals express concerns about their financial security, job prospects, and ability to achieve their goals. Economic stressors can exacerbate existing mental health issues and contribute to feelings of anxiety and hopelessness about the future (Dundon & Rieger, 2020).
Social and Political Climate:
The social and political landscape also influences Gen Z’s mental health. Issues such as climate change, social justice, and political polarization are sources of stress and anxiety for many young people. The constant exposure to distressing news and social issues through digital media can contribute to feelings of overwhelm and helplessness. Moreover, discrimination and marginalization based on factors such as race, gender identity, and sexual orientation can exacerbate mental health disparities within the Gen Z population (Salerno et al., 2021).
Supporting Gen Z’s Mental Health:
Addressing the mental health needs of Gen Z requires a multifaceted approach involving individuals, communities, and institutions. Providing access to mental health resources and support services is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Schools and universities can implement mental health education programs and offer counseling services to support students’ well-being. Employers can prioritize work-life balance and create supportive environments that promote mental health in the workplace. Additionally, destigmatizing mental illness and fostering open conversations about mental health can help reduce barriers to seeking help and support.
Generation Z faces a unique set of challenges that impact their mental health and well-being. From the pressures of social media and academic performance to economic uncertainty and societal issues, Gen Z is navigating a complex landscape fraught with challenges. By understanding these challenges and implementing targeted interventions and support systems, we can work towards creating a healthier and more supportive environment for Gen Z’s mental health and well-being.
References:
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2018). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 12, 271-283.
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Stress in America™ 2020: A National Mental Health Crisis. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2020/report
- Dundon, E. F., & Rieger, K. L. (2020). The Impact of Economic Uncertainty on Mental Health: A Longitudinal Study of Young Adults during the COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(18), 6966.
- Salerno, J. P., Williams, N. D., & Gattamorta, K. A. (2021). LGBTQ+ college student mental health: A review. Journal of American college health, 69(3), 279-286.














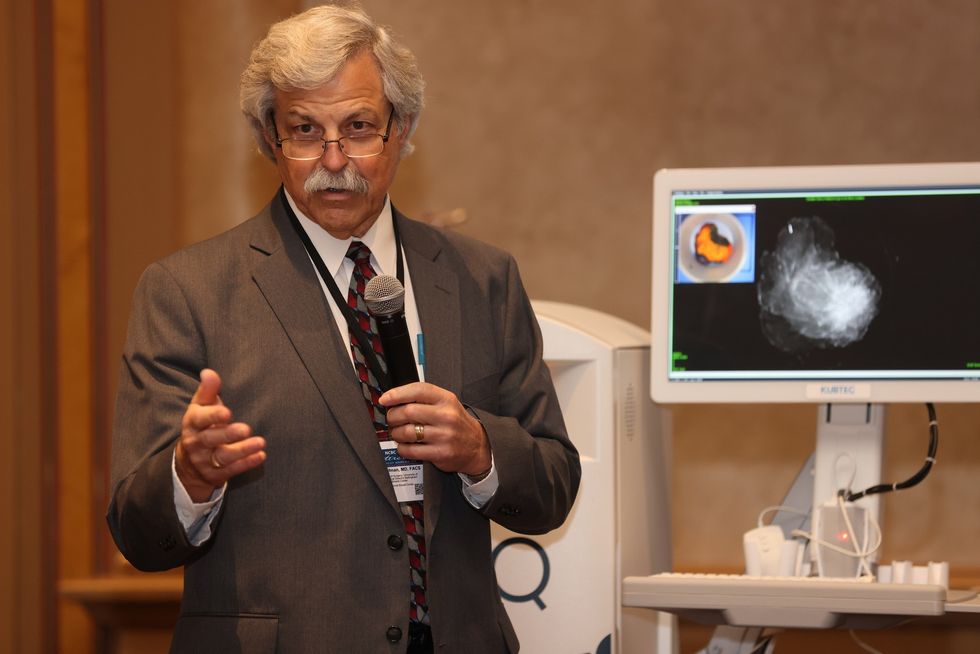 Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.
Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.

