Breast Cancer Survivor Eva Coleman faced chemotherapy headfirst by opting out of hair loss and opting into cold capping.
“At first, I was comfortable with the fact that I was going to lose my hair if I chose to do chemotherapy. Then, my oncologist explained that I didn’t have to lose it and that I could do cold capping. Although she matter-of-factly talked about this process, I had never heard of it before. My mother was sitting in the room when she began to share these details with me. It was like a little antenna went off in her head as my mom began to grasp everything; she was talking about cold capping,” said Coleman, who is a Telly award-winning producer with over 29 years of professional experience in television, radio, and newspapers.
Although Coleman initially wasn’t sold on the idea of cold capping, a few words from her mother would change her mind.
After much dialogue about hair loss, Coleman’s mother, Rosie Gray, said, “Baby, being bald won’t be a good look on you.”
It was these words, and being familiar with her mother’s brutal honesty, that made Coleman give cold capping a second consideration.
The idea of cooling the scalp to prevent hair loss started in Europe in 1998 and came to the United States a few years later. When cooled, the blood vessels in the scalp constrict, reducing blood flow to the hair follicles. That means less chemotherapy medication can get into the hair follicle cells. The cold also makes those cells less active, so chemotherapy drugs don’t target them as quickly. With less chemotherapy medicine in the follicles, the hair may be less likely to fall out.(1)
Due to the fact this is considered cosmetic, many insurance companies don’t cover the cost of this process.
“My mom, dad, and my brothers paid for it. We rented the system through a chemo cold capping company in Dallas. It was $425 a month, and I had four rounds of chemotherapy. Two of my rounds happened to be in the same month,” said Coleman.
For Coleman, cold capping was an eight-hour commitment during the days that she had chemotherapy. Although the actual infusion was only two and a half hours, the cold capping process started 50 minutes before the first drug was administered. Then, the cold capping was continued through the timeframe of her treatments. When the last drug was finished, cold capping was done for four more hours.
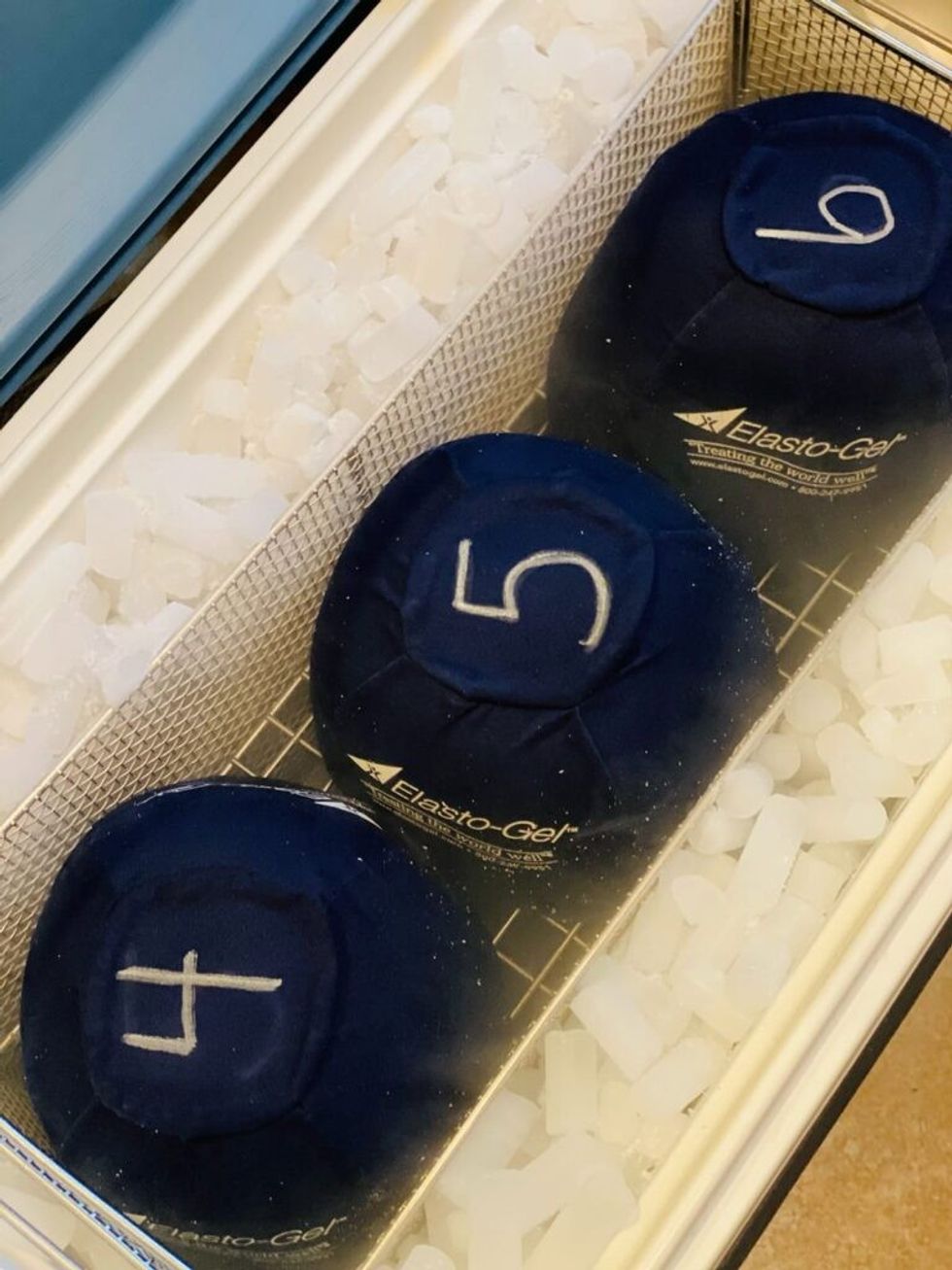
“Before her treatments, we placed a cold cap on her head, which was -30 degrees every 10 minutes. Then we would take it off. We had to saturate her scalp and hair with water before we started. During this process, we used a cooler that contained dry ice. We also wore gloves so we wouldn’t burn ourselves. We put a cap on her head, wrap her head up, and secure it tight. This caused her hair to freeze. I don’t know how she felt with -35 degrees every 10 minutes on her head, but I’m sure she was probably numb,” said Marion Forbes, who was Coleman’s stylist and acted as one of her cold capping buddies.
The gel-packed freezing cap is supposed to be between -30 and -32 degrees Celsius.
If you want to use a cold cap, your hair should be clean when you arrive at the infusion center. That means washing it the day before or the day of your treatment with a shampoo that’s free of paraben, silicones, and sodium laurel sulfate. On the day of your treatment, your hair must also be free of all products.(2)
On the first day of her chemotherapy, the cold capping company sent a trainer to help guide her designated capping buddies through the treatment.
“It was grueling because you’re putting these caps on your head that are extremely cold, and it’s a brain freeze every time. But I had to get used to it. It’s like when you step into an ice bath; when you step in, it’s extremely cold, and your body adjusts to it.
It’s the same with cold capping. Your body adjusts to it, but in this instance, by the time your body adjusts, it’s time to put a new cap on. So, there’s just a cycle of brain freeze, after brain freeze, after brain freeze. But in the grand scheme of things, it worked,” said Coleman.
One recent study examined the effects of the newer cold caps in women undergoing chemotherapy treatment for early-stage breast cancer. Of those who wore a cap consistently cooled to -32 degrees for 30 minutes before their chemotherapy treatment, throughout every chemo session, and for 90 to 120 minutes afterward, 66 percent experienced hair loss of 50 percent or less. That was compared to another group undergoing chemotherapy that did not use the caps. All of those patients lost more than half of their hair.(3)
Some research has also suggested that people with a thicker hair layer might be more likely to lose hair than those with a thinner layer of hair. This might be because the scalp doesn’t cool down enough due to the insulating effect of the hair.(4)
“I followed the requirements to the letter every single time. There are case studies that say that women who do cold capping properly retain at least 80 percent of their hair. To be honest, I feel like I retained more than that,” said Coleman.
While she was undergoing cold capping, her stylist treated her hair gently and made sure there wasn’t any excess tugging or heat applied to her hair.
This type of therapy only prevents hair loss on the scalp and doesn’t prevent loss elsewhere, such as a patient’s eyelashes, eyebrows, and other body hair.(3)
“I rocked this little twist out style for several months as I went through everything. But now, I can go back to regular styling. I think the recommendation was to wait eight weeks after your last chemotherapy treatment before going back to traditional styling,” said Coleman.
There remain some unanswered questions about the safety of scalp hypothermia. Some doctors are concerned that the cold could keep chemo from reaching any stray cancer cells lurking in the scalp. Some believe that the scalp cooling might protect cancer cells there and allow them to survive the chemo and keep growing. But in people who have had scalp hypothermia, reports of cancer in the scalp have been rare. More studies are needed to answer questions about long-term safety.(3)
“If I had to do it all over again, I think I would. I have to admit that it was tough because it’s a commitment. But again, I’m the type of person that, once I commit to something, I’m all in. I had a goal. The goal was to retain my hair, and I did that,” said Coleman.
Some of the minor side effects of cold capping include: chills, headaches, scalp irritation, and neck and shoulder discomfort.(3)
Sources
1:https://news.sanfordhealth.org/cancer/cold-capping-improving-confidence-during-cancer-fight/
2: https://www.ucsfhealth.org/treatments/cold-caps-to-reduce-chemo-hair-loss
4: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/managing-cancer/side-effects/hair-skin-nails/hair-loss/cold-caps.html