I don't know about everyone else, but there is nothing better than a maraschino cherry on top of an ice cream sundae. I'm also a sucker for ice cream and candy, but it seems like some of my favorite foods are soon going to be getting a makeover. For decades, Red Dye 3 (also known as erythrosine) has been a contentious ingredient in food and consumer products. Recently, this synthetic dye has been banned in the United States, sparking significant public discourse about food safety and regulatory practices. There is a history of Red Dye 3. There are reasons for its prohibition, and its implications for consumers and manufacturers.
What is Red Dye 3?
Red Dye 3 is a synthetic food coloring derived from petroleum. It has been widely used in candies, baked goods, beverages, cosmetics, and medications to impart a bright red hue. Despite its aesthetic appeal, concerns about its safety have loomed for years. it is important to note that Red Dye 3 isn't limited to just foods. It can also be found in medications such as Gabapentin (a nerve pain medication), Prozac (an antidepressant), and Acetaminophen.
The Scientific Concerns
Scientific studies have linked Red Dye 3 to various health risks, particularly cancer. A study in 1985 conducted by the National Toxicology Program (NTP) found that high doses of erythrosine caused thyroid tumors in male rats (NTP, 1985). These findings led the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ban its use in cosmetics and externally applied drugs in the same year. However, the dye continued to be permitted in food and ingested medications, much to the dismay of health advocacy groups.
The Regulatory Shift
In 2023, mounting public pressure and evolving research prompted the FDA to reassess Red Dye 3. Advocacy organizations, including the Environmental Working Group (EWG), highlighted the inconsistencies in allowing a substance with carcinogenic potential in food while banning it in cosmetics. The FDA’s decision to ban Red Dye 3 from consumables reflects a growing emphasis on precautionary measures in food safety regulations.
International Context
The U.S. is not the first country to take action against Red Dye 3. In the European Union, erythrosine has faced stringent restrictions for decades under the bloc’s rigorous food safety laws. Other countries, including Japan, have also imposed limits on its use. The U.S. ban aligns its policies more closely with global standards.
Implications for Manufacturers and Consumers
For manufacturers, the ban presents logistical and financial challenges. Reformulating products to exclude Red Dye 3 will require identifying suitable natural or synthetic alternatives. Options like beet juice, paprika extract, and other plant-based colorants are increasingly being explored.
Consumers, particularly parents of young children, have welcomed the ban as a step toward safer food. However, critics argue that the FDA should have acted sooner, given the long-standing evidence of harm.
What’s Next?
The ban on Red Dye 3 doesn't go into effect until 2027, but this does underscores the importance of ongoing research and vigilance in food safety. It also raises broader questions about the regulation of other synthetic dyes still in use, such as Yellow 5 and Blue 1, which have also faced scrutiny for potential health risks.
The prohibition of Red Dye 3 marks a pivotal moment in food safety policy. By prioritizing consumer health and aligning with international standards, the FDA has taken a significant step forward. However, this decision also serves as a reminder of the need for proactive regulation and transparency in addressing potential health risks associated with synthetic additives. It's worth it to be conscious of what you put into your body.
What contains Red Dye 3?
These are some of the products that contain Red Dye 3 (for more information visit the FDA's Site):
Cakes and candies
- Entenmann's Little Bites Party Cake Mini Muffins
- McCormick Red Food Color
- Betty Crocker Rainbow Sprinkles
- Hot Tamales Fierce Cinnamon Candy
- PEZ Assorted Fruit Candy
- Dubble Bubble Twist Bubble Gum
- Trolli Sour Crunchy Crawlers
- Brach's Classic Candy Corn
- PEEPS, Pink Marshmallows
- Some red velvet snack cakes
Dairy and Frozen Desserts
- Strawberry-flavored milk
- Certain ice cream flavors and frozen yogurt
- Ice pops and frozen fruit bars
Fruit Products
- Maraschino cherries
- Some fruit cocktails
Beverages
- Yoo-hoo Strawberry Drink
- Certain sodas and fruit-flavored drinks
Medications and Supplements
- Some cough syrups
- Gummy vitamins
- PediaSure Grow & Gain Kids' Ready-to-Drink Strawberry Shake
References
- National Toxicology Program (1985). Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Erythrosine (CAS No. 16423-68-0). Retrieved from NTP.
- Environmental Working Group (2023). Advocacy for Safer Food Additives. Retrieved from EWG.
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Food Additive Safety Assessments. Retrieved from EFSA.
- Food and Drug Administration














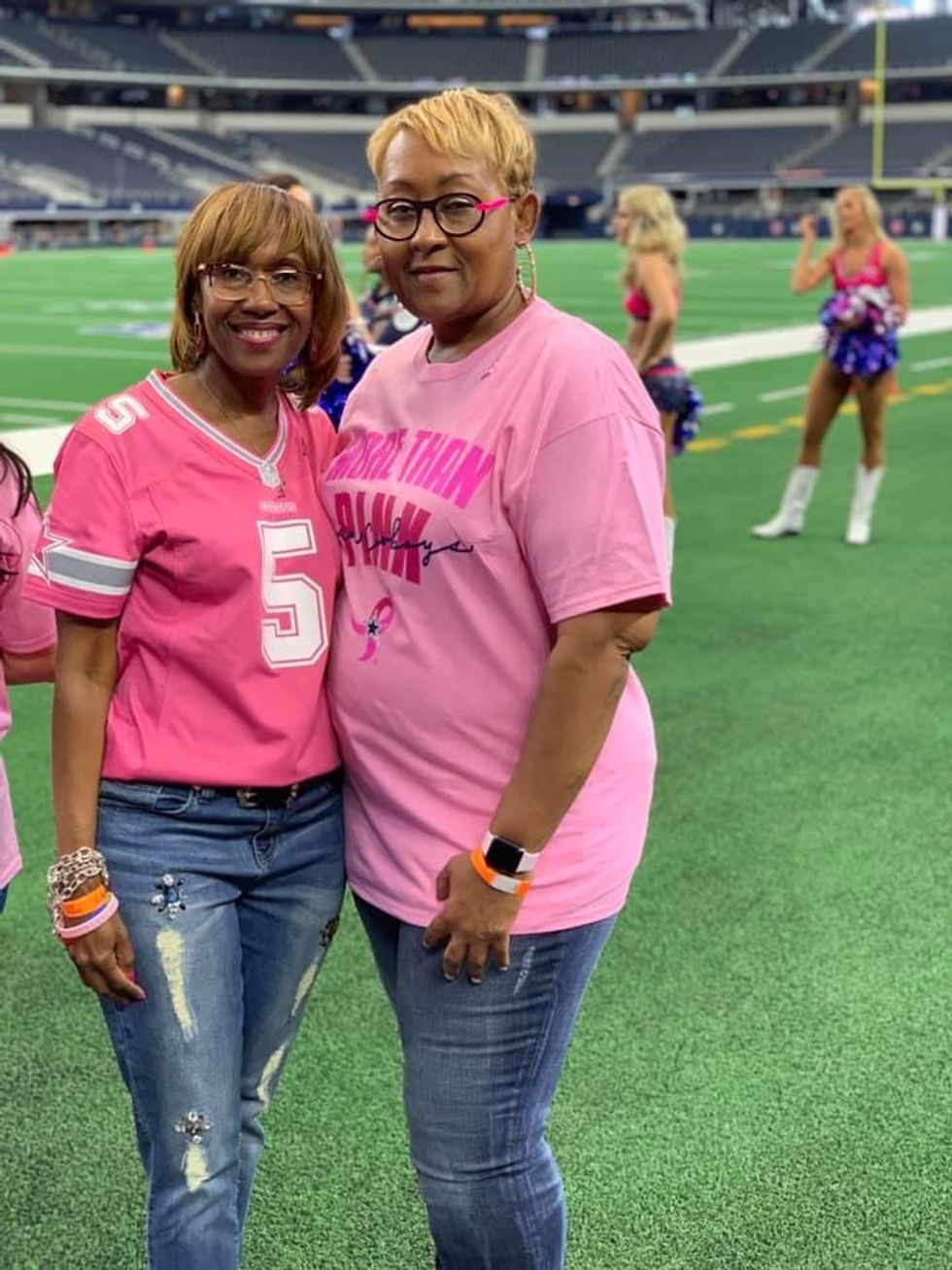 Ragina Ireland has been lovingly supported throughout her cancer journey by her sister, Johnnie Ireland. Four years ago, Ragina took a Cancer Genetic Risk Assessment test to help give her sister a clearer understanding of her own risk for developing breast cancer.
Ragina Ireland has been lovingly supported throughout her cancer journey by her sister, Johnnie Ireland. Four years ago, Ragina took a Cancer Genetic Risk Assessment test to help give her sister a clearer understanding of her own risk for developing breast cancer. 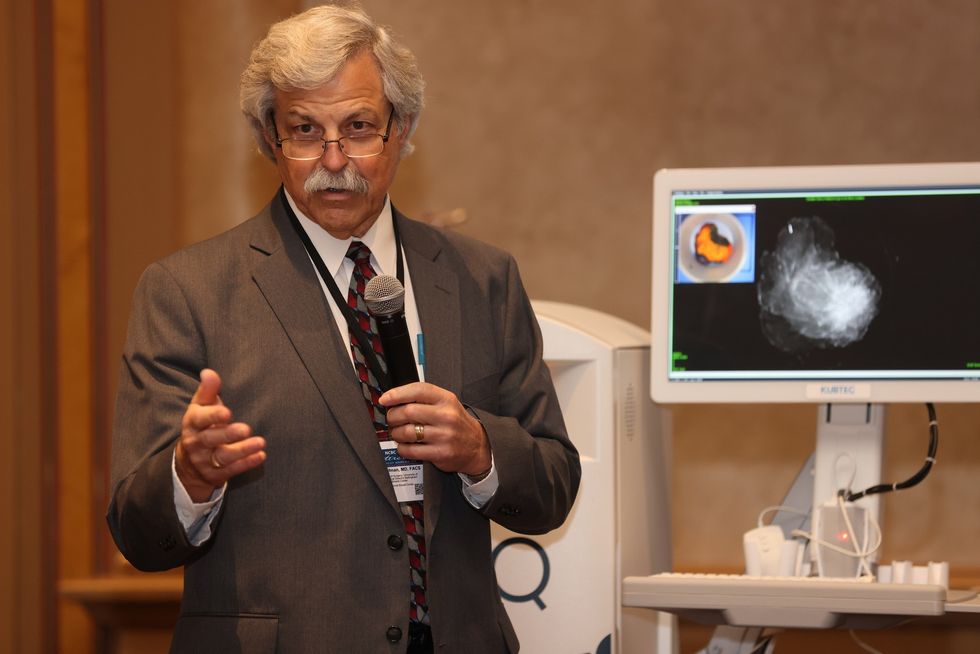 Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.
Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.