The digital age has transformed how children grow, learn, and interact. Devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops offer children access to limitless information, entertainment, and social connections. While technology can enhance learning and creativity, it also poses significant risks. As children spend more time online, they face dangers ranging from cyberbullying and screen addiction to exposure to inappropriate content and online predators. This article explores these risks and offers guidance for parents and guardians on how to protect children in the digital world.
1. Screen Addiction and Its Effects on Development
One of the most prominent concerns in the digital age is screen addiction. Children, particularly younger ones, can quickly become engrossed in the interactive nature of screens, often at the expense of other developmental activities such as physical play and face-to-face socialization.
Research shows that excessive screen time can negatively affect cognitive development, attention spans, and language skills. According to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics, toddlers and preschoolers who spent more time on screens had lower scores in developmental screenings, particularly in communication, motor skills, and problem-solving .
Additionally, prolonged screen exposure can disrupt sleep patterns, particularly when devices are used before bedtime. The blue light emitted by screens can suppress melatonin production, making it harder for children to fall asleep and negatively impacting their overall health .
2. Cyberbullying and Online Harassment
Cyberbullying is a growing issue, with children and teens facing harassment, humiliation, and threats online. Unlike traditional bullying, cyberbullying can happen 24/7 and in any location, as long as a child has access to a device. It can also reach a wider audience, with harmful messages or embarrassing images being shared across social media, leaving lasting emotional damage.
A 2020 survey by the Cyberbullying Research Center found that 37% of students aged 12–17 had experienced cyberbullying at some point in their lives. Victims of cyberbullying are at higher risk for mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts .
Unfortunately, many children who experience online harassment do not report it to parents or teachers, fearing retribution or that their devices will be taken away. This secrecy can exacerbate feelings of isolation and helplessness.
3. Exposure to Inappropriate Content
The internet provides access to vast amounts of information, but not all of it is suitable for children. Despite parental controls, many kids inadvertently encounter inappropriate content, including violent videos, pornography, or harmful ideologies.
Early exposure to such material can be damaging. Studies indicate that children exposed to violent media content are more likely to display aggressive behaviors or become desensitized to violence . Exposure to sexual content can also distort their understanding of healthy relationships and sexuality, leading to risky behaviors later in life.
Even platforms designed for kids, such as YouTube Kids, have faced criticism for failing to filter out inappropriate or disturbing content, exposing children to harmful material that may slip past parental filters .
4. Online Predators and Privacy Risks
One of the most alarming dangers for children in the digital age is the risk of online predators. Social media platforms, online games, and chat rooms offer spaces where predators can target children, posing as peers or offering fake friendships. Grooming—a process where predators build trust with children to exploit them sexually or financially—is a growing concern, particularly as kids spend more unsupervised time online.
The National Center for Missing & Exploited Children (NCMEC) reports a significant rise in online enticement and child exploitation cases in recent years. In 2020 alone, the organization received over 21.7 million reports of child sexual exploitation, much of it occurring through online platforms .
Additionally, children may not fully understand the importance of protecting their personal information online. Many are willing to share details such as their location, school, or other identifying information, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation or identity theft. Social media platforms and gaming communities can become entry points for bad actors to engage with children in inappropriate ways.
5. Impact on Mental Health and Social Development
Children's mental health is increasingly affected by their digital lives. The rise of social media platforms like Instagram, Snapchat, and TikTok has intensified the pressure on kids to present a "perfect" version of themselves. This pressure can lead to feelings of inadequacy, anxiety, and depression, especially as children compare their lives to the carefully curated posts of peers and influencers.
Research published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health found that frequent social media use was associated with poor mental health outcomes in adolescents, particularly in girls. The study noted that social media can disrupt sleep, increase exposure to cyberbullying, and contribute to body image issues, leading to mental health problems .
Moreover, while digital platforms can provide opportunities for social interaction, they can also hinder face-to-face communication skills. Excessive screen use can reduce the quality and frequency of real-life social interactions, impeding the development of essential social skills, such as empathy and active listening.
6. Data Collection and Surveillance
Children are increasingly being targeted by advertisers and tech companies that collect vast amounts of data on their online activities. While many parents assume that children's apps and websites are safe, a 2019 report by Common Sense Media found that many platforms collect personal data, often without parental consent, in violation of child privacy laws such as the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).
This data collection can be used to serve targeted ads, manipulate children's spending behaviors in games (such as in-app purchases), and track their habits over time. The long-term effects of growing up under such surveillance remain unclear, but they raise concerns about privacy and consumer rights.
How to Protect Children in the Digital Age
While the digital world poses significant dangers, there are steps parents and guardians can take to safeguard their children:
- Establish Clear Rules and Boundaries: Set screen time limits and establish boundaries about which websites, apps, and social media platforms children can access. Make sure these rules are consistent and age-appropriate.
- Use Parental Controls and Monitoring Tools: Most devices and platforms offer parental controls that allow you to filter content and monitor usage. Apps such as Qustodio and Net Nanny provide robust options for keeping tabs on children's online activity.
- Open Communication: Foster an open dialogue about internet safety. Encourage children to speak up if they encounter something inappropriate or if someone makes them uncomfortable online. Make sure they understand the dangers of sharing personal information.
- Teach Critical Thinking: Educate children on how to recognize online dangers such as fake news, scams, and phishing attempts. Critical thinking skills can help children navigate the digital world more safely and responsibly.
- Lead by Example: Children model their behavior after their parents. Set a good example by maintaining healthy screen habits, engaging in real-world activities, and putting devices away during family time.
The digital age offers both incredible opportunities and significant dangers for children. While technology can enhance learning, creativity, and socialization, it also introduces risks such as screen addiction, cyberbullying, and online predators. By taking proactive steps to educate, monitor, and communicate with children, parents and guardians can help ensure that their digital experiences are safe and enriching.
Sources:
- Madigan, S., Browne, D., Racine, N., Mori, C., & Tough, S. (2019). Association Between Screen Time and Children's Performance on Developmental Screening Tests. JAMA Pediatrics. Retrieved from JAMA.
- Patchin, J. W., & Hinduja, S. (2020). Cyberbullying: Identification, Prevention, and Response. Cyberbullying Research Center. Retrieved from Cyberbullying.org.
- Gentile, D. A., & Bushman, B. J. (2012). Violent Video Games and Aggression. Pediatrics, 129(2), 252-259.
- NCMEC. (2020). Online Enticement Reports Rise in 2020. National Center for Missing & Exploited Children. Retrieved from NCMEC.
- Kelly, Y., Zilanawala, A., Booker, C., & Sacker, A. (2019). Social Media Use and Adolescent Mental Health: Findings From the UK Millennium Cohort Study. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. Retrieved from The Lancet.
- Common Sense Media. (2019). Privacy Risks in Children's Apps. Retrieved from Common Sense Media.












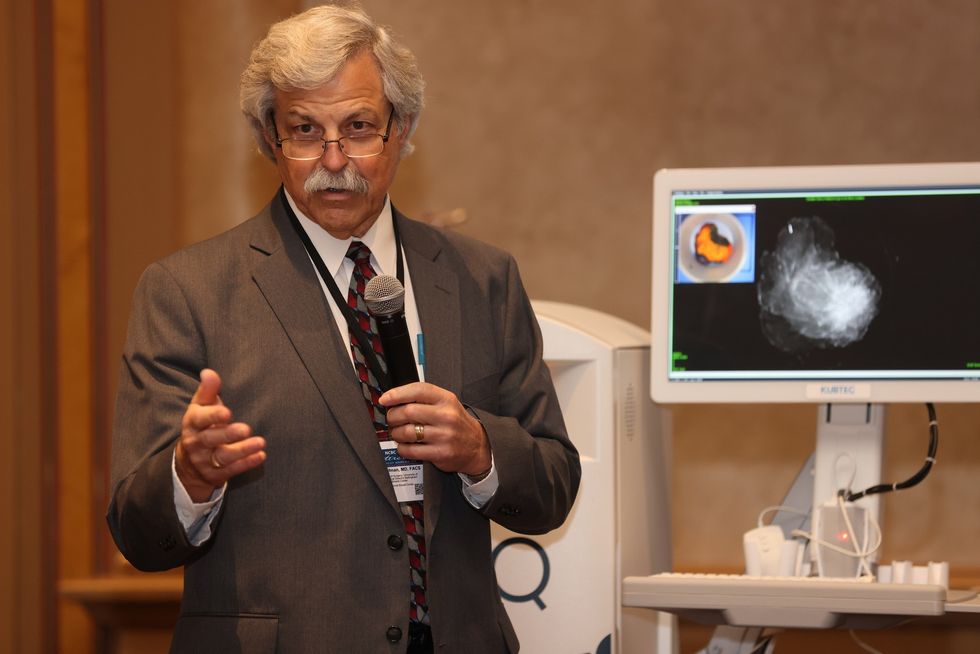 Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.
Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.

