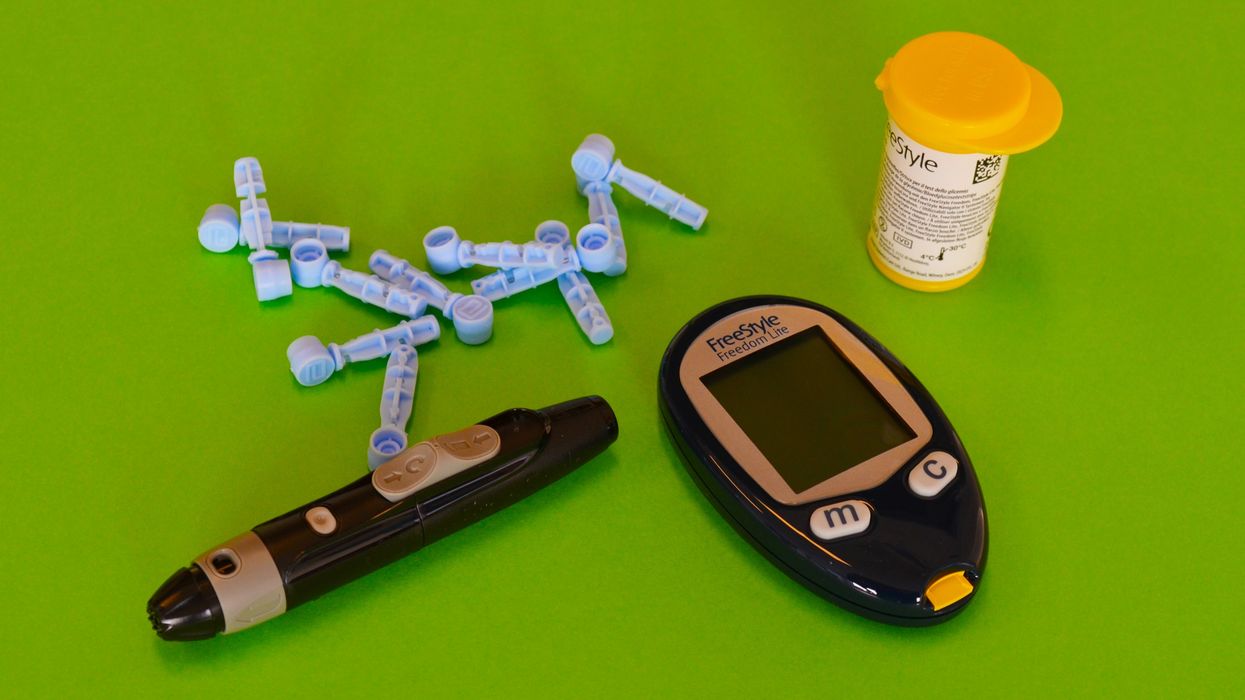
Diabetes awareness month falls at a very apropos time. We are getting into the holiday season when we eat candy, cookies, and tons of food. According to the CDC there are 38.4 million Americans with diabetes (that's 11% of the population). 23% of those people are undiagnosed. Even worse, the CDC has said that the rate of diagnosis has increased at an alarming rate in the United States. Every November, American Diabetes Month takes center stage as a nationwide effort to increase awareness about diabetes—a chronic disease impacting millions of Americans. Sponsored by organizations such as the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and supported by public health campaigns, this observance focuses on prevention, early detection, and supporting those living with diabetes.
The Two Different Diabetes Types
Diabetes is a group of diseases that affect how the body processes blood glucose (sugar), with two main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, usually developing in childhood or early adulthood.
- Type 2 Diabetes is a condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough, commonly linked to lifestyle factors.
【1】【2】.
Why Awareness Matters
American Diabetes Month plays a critical role in:
- Highlighting Prevention and Education:
Many Type 2 diabetes cases are preventable with lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, regular exercise, and weight management. Programs like the CDC’s National Diabetes Prevention Program have shown that lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes by as much as 58% 【2】. - Reducing Health Disparities:
Diabetes disproportionately affects certain populations, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Pacific Islanders. These groups are more likely to develop diabetes and experience complications such as kidney disease, vision loss, and heart disease 【3】. Awareness campaigns during November aim to reduce these inequities by promoting accessible care and culturally tailored interventions. - Encouraging Early Detection:
Early diagnosis of diabetes and prediabetes can prevent or delay complications. Blood sugar screenings and increased public awareness of symptoms—such as frequent urination, extreme thirst, and fatigue—are key components of the campaign 【4】. - Showcasing Advances in Research and Technology:
The month also highlights ongoing advancements in diabetes treatment, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems and artificial pancreas devices. Research into potential cures continues to offer hope for millions 【1】【5】.
Each year, the ADA spearheads awareness efforts under a unifying theme. Recent campaigns like “This Is Diabetes” have featured personal stories to shed light on the real-life challenges and triumphs of managing diabetes. Social media hashtags, including #DiabetesAwarenessMonth, further amplify the message and engage a broader audience.
How can you help? Individuals, organizations, and communities can support American Diabetes Month in various ways:
- Schedule a Screening: Routine blood glucose tests can detect diabetes or prediabetes early.
- Educate Others: Share information about risk factors, such as obesity, family history, and age.
- Get Active: Physical activity is a cornerstone of diabetes prevention and management.
- Support Research and Advocacy: Donations to diabetes organizations help fund research and advocacy efforts aimed at improving care and affordability.
With diabetes on the rise globally, American Diabetes Month provides a crucial opportunity to confront the disease head-on. Through education, advocacy, and community engagement, we can reduce its prevalence, improve the quality of life for those affected, and support groundbreaking research.
To learn more, visit the American Diabetes Association (ADA) at diabetes.org or the CDC's diabetes resources at cdc.gov/diabetes.
References
- CDC. (2023). National Diabetes Statistics Report. Retrieved from cdc.gov.
- American Diabetes Association. (2023). Prevention. Retrieved from diabetes.org.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). Health Disparities and Diabetes. Retrieved from niddk.nih.gov.
- Mayo Clinic. Diabetes: Symptoms and Causes. Retrieved from mayoclinic.org.
- JDRF. Advances in Diabetes Research. Retrieved from jdrf.org.






 Karla Mingo believes that her greatest gift as a cancer survivor is the ability to live with gratitude and thankfulness.
Karla Mingo believes that her greatest gift as a cancer survivor is the ability to live with gratitude and thankfulness.