In a world that is constantly moving, finding ways to engage our minds in a fun and entertaining way is more important than ever. Game shows like Jeopardy! and Wheel of Fortune do just that! Not only are these beloved TV staples exciting, but they also provide a unique opportunity to boost cognitive health. Let’s dive into the delightful reasons why tuning in to these iconic shows could be just what your brain needs.
1. Mental Stimulation on the Daily
Watching Jeopardy! is like taking your brain to the gym. The rapid-fire questions in categories like history, science, and pop culture force viewers to recall information quickly and stay mentally engaged. Studies suggest that activities requiring mental effort, such as problem-solving and memory recall, are effective in strengthening cognitive functions . Jeopardy! offers exactly this kind of engagement, challenging us with trivia questions that sharpen recall and information processing.
2. Wordplay and Puzzle Solving
If you’re more into spinning the wheel, Wheel of Fortune has a different, yet equally exciting, cognitive benefit. The puzzles in Wheel of Fortune encourage players to think critically and use pattern recognition skills, essential for maintaining cognitive sharpness. According to cognitive research, engaging in word puzzles can significantly improve brain function by enhancing verbal skills and memory . Every time you guess a letter or solve the puzzle, your brain is making connections that keep it flexible and resilient.
3. Social Connection and Mental Wellness
Watching game shows can also foster social connections, which are vital for mental health. Many viewers enjoy watching these shows with family and friends, or even participating in online forums and discussions about their favorite episodes. Studies show that social interaction, even over shared television programs, can contribute to emotional well-being and cognitive longevity . The camaraderie and sense of accomplishment shared with others while shouting out answers from the couch create a positive mental health boost.
4. Encouraging Lifelong Learning
Game shows like Jeopardy! expose viewers to a wide range of new topics. From obscure historical facts to scientific breakthroughs, the show encourages viewers to remain curious and continue learning. This type of intellectual curiosity is a key component of lifelong cognitive health. Researchers note that learning new things and challenging the brain consistently over time can protect against cognitive decline .
5. Boosting Confidence and Motivation
Successfully answering questions or solving puzzles (even just from your living room) can provide a wonderful confidence boost. It’s that feel-good moment when you realize, “Hey, I knew that!” These small victories, over time, can increase self-confidence and motivate viewers to engage in other brain-stimulating activities like reading, problem-solving, or learning a new hobby.
A Fun Brain Boost
Game shows like Jeopardy! and Wheel of Fortune may be entertainment, but they offer much more than just fun. They engage our brains, encourage social connections, and stimulate lifelong learning, all while boosting cognitive function. So the next time you tune in, know that your brain is getting a delightful workout. It’s not just a show—it's an investment in your mental health!
References:
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2022). Mental stimulation and cognitive health: Why challenging your brain keeps it sharp. Retrieved from [harvardhealth.com]
- American Psychological Association. (2021). The cognitive benefits of puzzles and problem-solving activities. Retrieved from [apa.org]












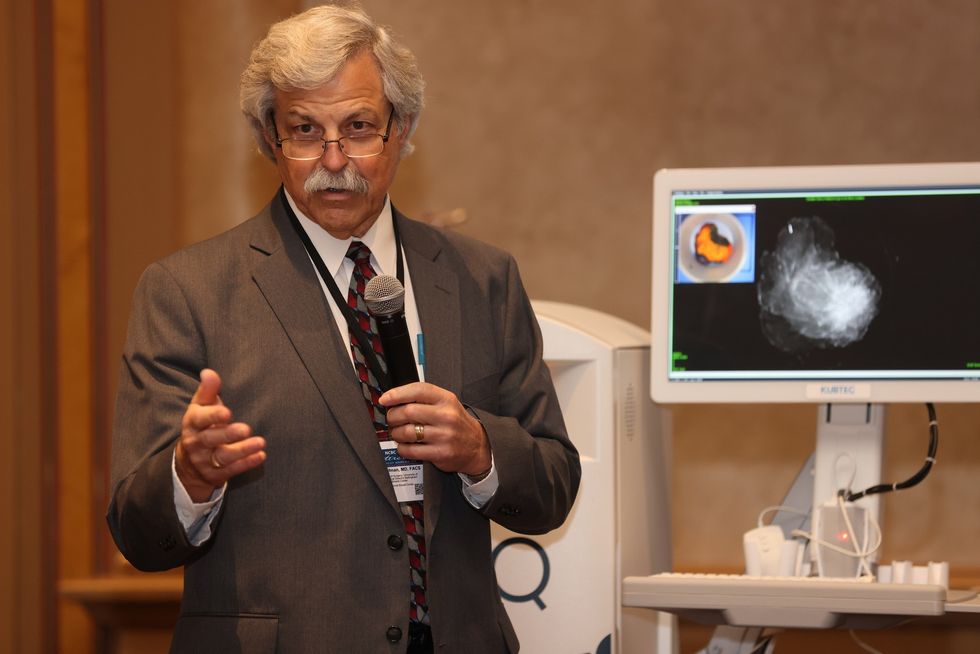 Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.
Dr. Cary S. Kaufman teaches the "Essentials of Oncoplastic Surgery" course through the National Consortium of Breast Centers, providing breast surgeons around the world with advanced techniques for optimal breast surgery outcomes.

