he Ashkenazi Jewish community, with a rich history and a strong sense of cultural identity, faces specific health challenges that have gained increasing attention in recent years. While this community is known for its resilience, its members are not immune to certain inherited genetic conditions that can impact health and wellbeing. In this article, we will explore the unique health issues within the Ashkenazi community, the efforts being made to address them, and the importance of raising awareness.
Genetic Predisposition
One of the most well-known health issues in the Ashkenazi community is a higher prevalence of certain genetic disorders, particularly those involving the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. These mutations significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer. Additionally, Ashkenazi Jews are at an increased risk of genetic conditions like Tay-Sachs disease, Gaucher disease, and Canavan disease. These conditions can have a profound impact on the health of individuals within the community.
The Importance of Genetic Testing
Awareness and early intervention are vital in managing the health issues in the Ashkenazi community. Genetic testing is a powerful tool that can help identify individuals at higher risk for these conditions. With this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions about preventive measures, including regular screenings, lifestyle choices, and even surgical interventions in some cases. Genetic testing is becoming increasingly accessible and is a proactive step towards better health outcomes.
Community Outreach and Education
Community organizations, healthcare providers, and advocacy groups have been actively working to increase awareness and education within the Ashkenazi community. Seminars, workshops, and informational campaigns are held to provide individuals with the knowledge and resources they need to make informed decisions about their health. Many organizations also offer support and counseling for those who are found to be carriers of genetic mutations.
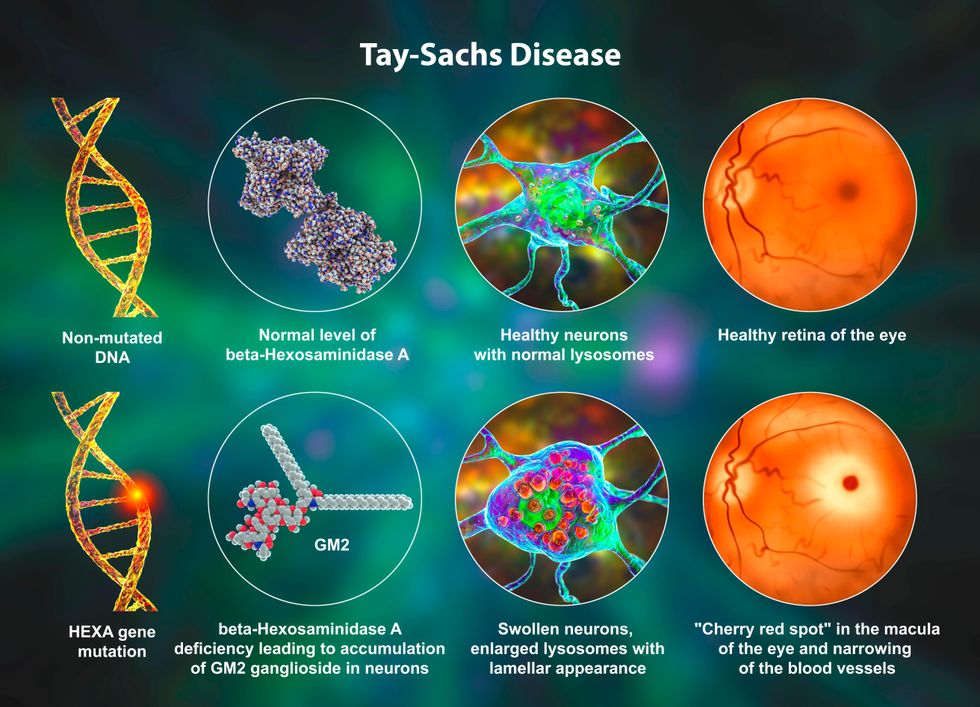
Preventive Measures and Wellness Initiatives
Promoting wellness and healthy living within the Ashkenazi community is another critical aspect of addressing health issues. Encouraging regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Additionally, healthcare providers are working to develop personalized healthcare plans that take into account an individual's genetic predisposition, tailoring preventive measures to their unique needs.
Research and Advances in Treatment
Ongoing research in the field of genetics and healthcare is bringing hope to the Ashkenazi community. Scientific advancements are leading to improved treatments and interventions for various genetic conditions, offering better prospects for those affected. Participation in clinical trials and collaborative research efforts is an important part of the path forward.
The Ashkenazi community's health issues are a significant concern, but they are not insurmountable. By prioritizing awareness, genetic testing, community outreach, and a focus on overall wellness, this resilient community can take proactive steps toward better health outcomes. In an ever-evolving healthcare landscape, it's crucial to continue working collaboratively to support those affected and create a healthier future for all members of the Ashkenazi community.









 Dr. Jay Harness, MD, FACS, founder of Cancer Fitness, believes that when a woman begins exercising after breast cancer, it marks the start of her personal reconstruction journey.
Dr. Jay Harness, MD, FACS, founder of Cancer Fitness, believes that when a woman begins exercising after breast cancer, it marks the start of her personal reconstruction journey.